
Chronic Kidney Disease
Approximately 11% of U.S. adults have CKD, many of whom are elderly. The condition is usually asymptomatic until its advanced stages. Most cases of CKD are associated with diabetes or hypertension.
eGFR is considered the best screening tool for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
eGFR Calculator
Treatment of early stages of CKD is generally targeted to comorbid medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease, to reduce the risk for complications and progression of CKD.
The National Kidney Foundation recommends assessing risk for CKD in all patients and doing the following for those at increased risk: measure blood pressure, test serum creatinine levels, test urine albumin levels, and examine urine for erythrocytes and leukocytes1
|
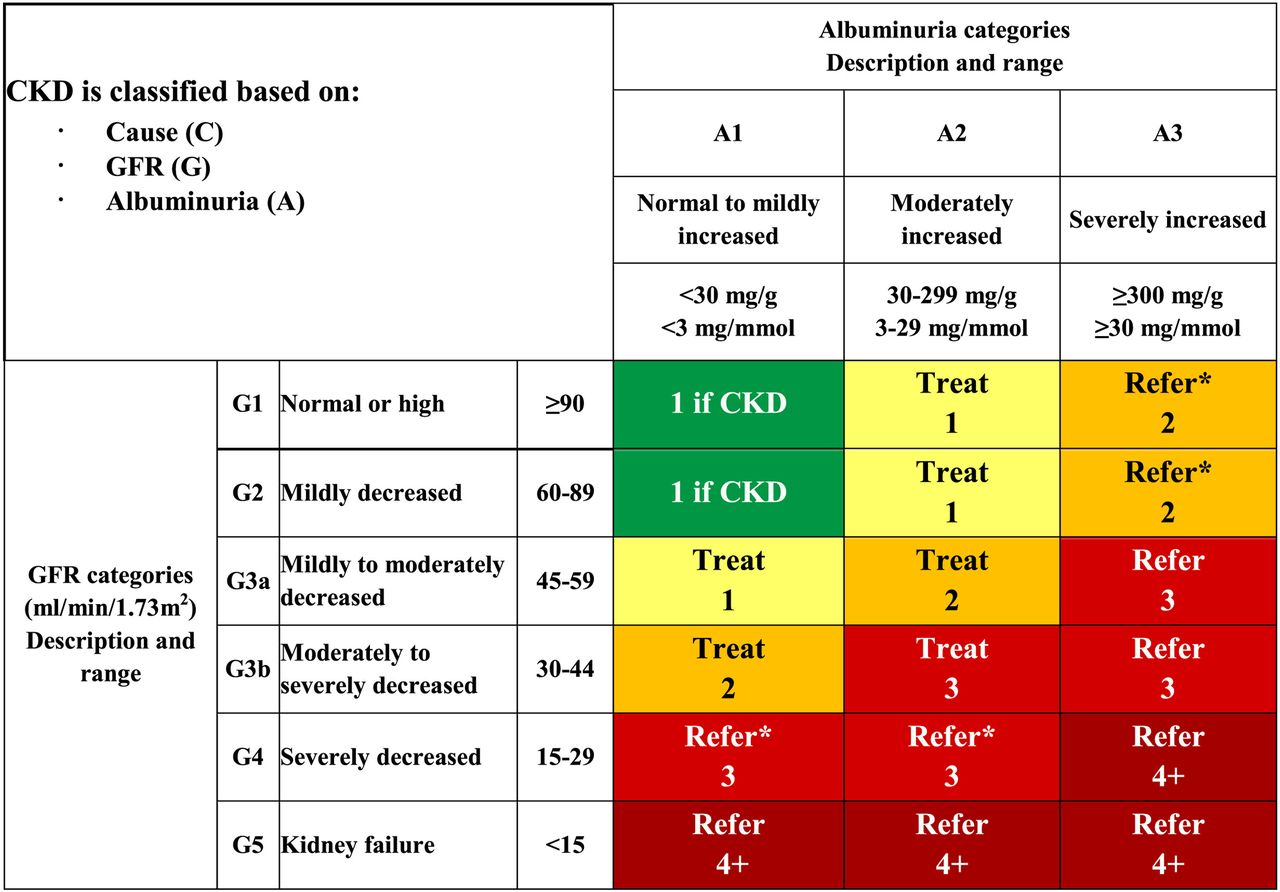
CKD CRITERIA:
Any of the following must be present for 3 months or more
- Urinary albumin to creatinine ratio > 30 mg/g
- Markers of kidney damage (like radiologic abnormalities)
- GFR < 60 mL/min/1.73m2
CKD RISK FACTORS:
Modifiable:
- Diabetes, Hypertension, history of AKI, frequent analgesic use
Non-modifiable:
- Family history of kidney disease, diabetes, or hypertension, age 60 or older, race/ethnic minority status
|
|
WHEN TO REFER:
- Acute kidney injury or abrupt sustained fall in GFR
- GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2 or GFR categories G4 - G5
- Persistent albuminuria measured by Albumin: Creatinine Ratio (ACR > 300 mg/g)
- Atypical progression of CKD (sustained decline of GFR by more than 5 mL/min/1.73m2/year)
- Urinary red cell casts, RBC more than 20 per HPF sustained and not readily explained
- Hypertension refractory to treatment with 3 or more anti-hypertensive agents
- Persistent abnormalities of serum potassium
- Recurrent or extensive nephrolithiasis
- Hereditary kidney disease
Thank you, Dr. Stephen Clyne for the content of this Clinical Corner. He may be reached via: Michigan Kidney Consultants, PC, 44200 Woodward Avenue, Suite 209, Pontiac, MI 48341, (248) 253-0330
Reference:
1. National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification, and Stratification. New York: National Kidney Foundation; 2002.
Download Clinical Corner